
Technology design and programming
World Economic Forum published top 10 job skills of tomorrow. In our blog series you will get a deeper dive into each one of these skills of tomorrow.
Technology design and programming
Technology is the cornucopia that has brought mankind from famine, nuclear war, shortage of raw materials and epidemics towards sustainable widespread prosperity. Automatic data processing is one of the success stories of the past century. To the disappointment of employers, the way to train cheap programmers has not been found, despite attempts.
Inherent uncertainty
Developing new technologies is inherently difficult. In research and development, the end result is not predictable and it is not even certain that it is achievable. Technologies are based on natural sciences and mathematics, which are exact disciplines. The laws of nature exist regardless of man, and if our plan does not respect them, the solution will not work.
Success in technological development requires adapting many influential factors of the same solution. Let’s think of batteries as an airplane energy storage. The battery must be lightweight, reasonable in price, sufficient in capacity and it can be rechargeable quickly. Its life cycle must be long and as maintenance-free as possible. It must not be dangerous in the case of accidents, and in especially not in itself, pose a danger to people and property. It may even be that storing energy in ions cannot replace its transport as chemical compounds such as hydrocarbons used as fuels.
No major productivity leaps are expected in software development, as the difficulty is in thinking, not in writing code[1]. The problem is the same as writing a book. The hardest part is deciding what to write. Better word processors do not make anyone a Nobel writer. Outsourcing word processing to low-cost labor is unlikely to reduce the total cost of writing.
Culture of experimentation
Natural sciences are based on observations. If your theory doesn’t match the findings, it’s wrong, no matter how famous and respected you are. In our design work, we rely on previous observations and the experience gained from them. Bridges, roofs and high-rises rarely collapse because millions of similar ones have been built before.
Experience is enshrined in standards, and the focus is on monitoring compliance with them. The other side of the standards is the shackle of creativity. It is difficult to bring new innovations to market because changing standards is behind difficult bureaucracy. The standards prevent new competitors from entering the market.
Regulation is most often justified by the protection of consumers. Good-seeking regulations have done a lot of damage when they have been made without sufficient observational data. Mouldy schools are an example where making buildings air-tight causes moisture to accumulate in structures.
Logical integrity is central to mathematics. Technology solutions must also form a consistent whole. People find it uncomfortable [2] to use hydrogen from hydrocarbons as fuel to avoid the use of hydrocarbons, for example.
In software production, programmers perform a large number of tests that check the functionality of code logic. Nowadays, the driving of tests is automated, which means that the testing cost consists mainly of writing tests.
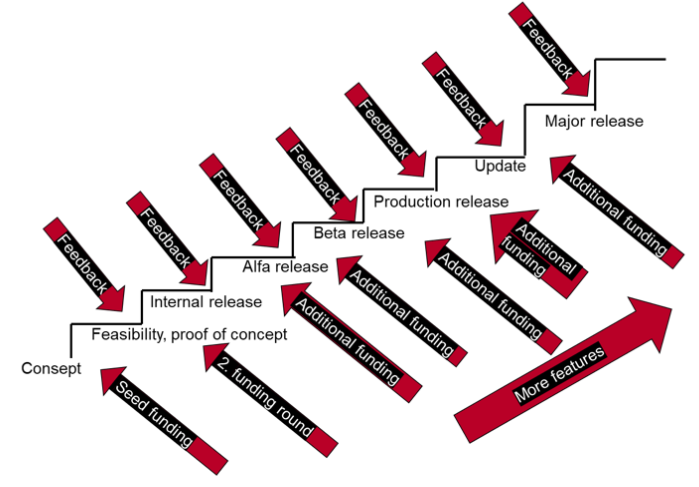
Designing a new product typically proceeds from ensuring the idea through several prototypes towards a product that is cautiously released. The number of product features and users increases as the development continues. A large number of R&D projects are fail fast. Before, for example, a self-driving car is finally placed on the market, it has been tested for millions of hours and it has driven billions of kilometers in various environments.
Do something different
According to McKinsey’s survey, business leaders are dissatisfied with their organizations’ ability to innovate. Company culture and the way they operate does not create conditions in which people could do something different [3].
Academic freedom in universities in the past has been replaced by strict performance guidance. Employment relationships are short-term and precarious. The number of publications is used as a measure of the results. As a consequence, there are a large number of certain research topics that can easily produce publications that go through peer review.
One patent office clerk produced more significant research a hundred years ago than millions of full-time researchers since him [4]. He managed to convince the critical scientific community through observations supporting his theories.
Dissidents create significant new inventions because significant new inventions require different thinking. See also [5]. Several organizations emphasize unity. Processes are standardized to optimize efficiency. Working methods are frozen with quality manuals. HR rewards obedience and punishes deviations. Failure leads to personal changes.
Dissent is difficult because the community creates a lot of pressure against it. The gatekeepers of publications censor differences. Freedom of speech is being shackled. Career progression can be difficult. The reward for success is small, if there is any.
We recognize things that are not allowed to be talked about. They are often driven by money and conflicts of interest. The innovator’s dilemma explains why it is easier for small external companies to develop products that compete with your own product [7]. So the internet calls came from Skype and not from telecommunications operators.
Abundance of options
Genetic diversity is nature’s way of surviving in an ever-changing environment. If there is a lack of food, smaller animals will survive better. If, on the other hand, there is plenty of food, natural selection favors larger animals.
Technological solutions are part of complex competing ecosystems. They often have unpredictable long-term effects that nullify the short-term benefits. Almost all major technology organizations work with many technology suppliers, integrators and vendors – sometimes hundreds of them [7]. In many cases, adaptability is more important than short-term cost benefits.
Even more broadly, centralized decision-making and centralized solutions involve great risks. In a decentralized model not all eggs are in the same basket. In a complex world, we can’t predict winners. By diversifying both our investments and our technology solutions, we reduce our risks.
We learned from history that nations thrive when consumers’ purchasing decisions guide the development and production of technologies [8]. There is a large competing group of alternative products and those buying with their own money are critical to their choices. Alternatives imposed by massive image marketing mostly benefit sellers. LED lights came into use quickly and undetected because they were good enough for consumers naturally. The advancement of electric cars, on the other hand, is slowing despite the high subsidies.
Genetic diversity is nature’s way of surviving in an ever-changing environment. If there is a lack of food, smaller animals will survive better. If, on the other hand, there is plenty of food, natural selection favours larger animals.
Programmer shortage
The underlying reason for the programmer shortage is that employers do not see the forest from the trees. Job advertisements are full of requirements for techniques whose skills are required. Because fashionable techniques are constantly changing, their experienced experts cannot exist.
Competitive tendering at the hourly rate favors cheap workers who have learned the desired things superficially. If the logical mindset required for all programming is lacking, the results are poor and learning the next technique is difficult.
Discussion
Today’s well-being comes from knowledge and good ideas. There is no shortage of raw materials, funding and labor. Instead of sending money, governments should promote the education of all mankind. In the words of an old metaphor: do not give a hungry man fish, but teach him how to fish.
References and additional readings
- Fred Brooks, The mythical man-month, 1975.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_dissonance
- https://hbr.org/2019/11/breaking-down-the-barriers-to-innovation
- https://www.ige.ch/en/about-us/the-history-of-the-ipi/einstein/einstein-at-the-patent-office
- Handbook of Scientific Dissidents: Asko M. Aurela: Tieteellisen toisinajattelijan käsikirja, Art House, 1993.
- https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/building-a-tech-services-ecosystem-to-deliver-products-not-applications
- Innovator’s dilemma https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Innovator%27s_Dilemma
- http://whynationsfail.com/summary/
– Pentti Virtanen

